俗话说:工欲善其事,必先利其器.要做好系统管理,使自己的工作更轻松更有效的话,一个好的监控工具是必不可少的了.在这里我向大家推荐一款我使用了4年多的、功能强大、可灵活定制的开源监控利器—nagios。
运维监控Nagios连载1:Nagios服务器的自我监控实现 http://net.it168.com/a2009/0309/267/000000267878.shtml 运维监控Nagios连载2:部署apache服务器 http://net.it168.com/a2009/0310/268/000000268103.shtml 运维监控Nagios连载3:部署、配置Nagios服务 运维监控Nagios连载4:Nagios监控mysql服务器 运维监控Nagios连载5:关键应用监控的重要策略
(一) 添加帐户,以用来运行Nagios。
当然也可以用root运行,但出于安全考虑而使用普通帐号来运行,并且不给这个账号分配shell登录权限. 1、 linux增加帐号的操作为 useradd nagios -s /sbin/nologin 添加帐号就自动生成同名组 nagios。 2、 freebsd增加帐号的操作为 pw groupadd nagios ; pw useradd nagios -g nagios -s /sbin/nologin. 注意:不要给nagios用户设置密码。 (二) 安装nagios软件 tar zxvf nagios-2.9.tar.gz cd nagios-2.9 ./configure -prefix=/usr/local/nagios —-with-nagios-user=nagios –with-nagios-group=nagios make all make install 执行完这个步骤后,程序会提示依次运行 make install-init , make install-commandmode ,make install-config 这几个命令。我们选取其中的两个来执行: make install-commandmode make install-config
跟一般的gnu源码软件安装相比,nagios的安装多了几个步骤(一般的软件运行到make install就算安装完了)。当然也可以连这两步都不执行,用手工赋予目录或文件权限,再手动创建配置文件,其效果完全相同。安装完nagios后,我们可以在安装目录/usr/local/nagios下生成下面的目录: bin Nagios执行程序所在目录,这个目录只有一个文件nagios etc Nagios配置文件位置,初始安装完后,只有几个*.cfg-sample文件 sbin Nagios Cgi文件所在目录,也就是执行外部命令所需文件所在的目录 share Nagios网页文件所在的目录 var Nagios日志文件、spid 等文件所在的目录
(三) 安装nagios插件 没有插件,nagios将什么作用也没有,插件也是nagios扩展功能的强大武器,除了下载常用的插件外,我们还可以根据实际要求编写自己的插件。Nagios的插件nagios-plugins-1.4.9在www.nagios.org上可以找到,接着我们用wget下载它。注意:插件与nagios之间的版本关联不大,不一定非得用nagios-plugins-1.4.9这个版本。下载完成后,安装它是很简单的:先执行配置 ./configure -prefix=/usr/local/nagios ,接着编译安装 make ; make install即可。这里需要说明一下的是在配置过程指定的安装路径是/usr/local/nagios,而不是/usr/local/nagios-plus,安装完成后,将在目录/usr/local/nagios生成目录libexec(里面有很多文件),这正是nagios所需要的。
#p#
(四) 配置nagios
配置是nagios最复杂的部分,让我们耐心一些,逐个处理,配置成功也不是什么难事。刚安装完成的nagios,其配置文件的目录是/usr/local/nagios/etc,下图是其etc目录的文件: 先把这些文件改名,如 cgi.cfg-sample改成cgi.cfg ,用命令cp cgi.cfg-sample cgi.cfg …依样把余下的几个*.cfg-sample都复制成*.cfg文件。从nagios2.6版开始,不用修改配置文件localhost.cfg就可以直接运行../bin/nagios -v nagios.cfg验证程序是否能正常运行(nagios2.5及以前版本的最小运行的配置文件是minimal.cfg,但需要修改这个文件多处才能验证成功)。当然,我们不能指望这个最小的配置文件能够满足实际的需求,因此,需要对现有的配置文件进行修改,其次增加自定义的一些配置文件。通过复制这些自带的模板文件,我们可以得出几个主要的配置文件,我们可以把它归类为:
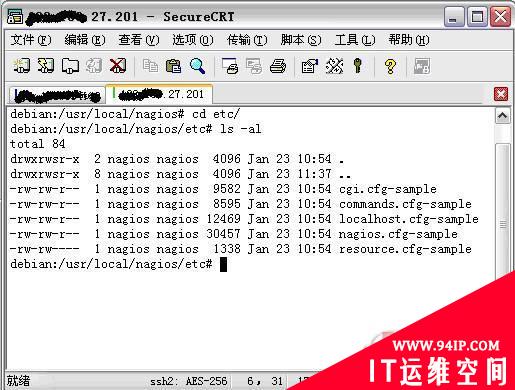
| 类型名 | 包含文件 | 作用 | 备注 |
| 主配置文件 | nagios.cfg | 定义和控制nagios行为 | 需要修改 |
| Cgi配置文件 | cgi.cfg | 浏览器执行诸如重启nagios服务等 | 修要修改 |
| 宏定义文件 | Resource.cfg | 定义插件路径 | 不需修改 |
| 命令定义文件 | Commands.cfg | 定义怎么发送短信、邮件等 | 需要修改 |
| 其他文件 | contactgroups.cfg, contacts.cfg,hostgroups.cfg,hosts.cfg,services.cfg | 监控对象配置文件,如主机配置文件、联系人配置文件等 | 主配置文件包含,手动创建 |
依照这个表格,我们逐一配置之。 1、修改主配置文件nagios.cfg.基于方便维护的原则,把各个配置目标单独放在文件中,如联系人信息在contacts.cfg中定义。Nagios.cfg文件比较长,我只把修改过的内容贴出来: #注释或删掉这行 #cfg_file=/usr/local/nagios/etc/localhost.cfg
#主机配置文件路径 cfg_file=/usr/local/nagios/etc/hosts.cfg
#//主机组配置文件路径 cfg_file=/usr/local/nagios/etc/hostgroups.cfg
#联系人配置文件路径 cfg_file=/usr/local/nagios/etc/contacts.cfg
#联系组配置文件路径 cfg_file=/usr/local/nagios/etc/contactgroups.cfg
#服务配置文件路径 cfg_file=/usr/local/nagios/etc/services.cfg
#监视时段配置文件路径 cfg_file=/usr/local/nagios/etc/timeperiods.cfg
#在web界面下重启nagios、停止主机/服务检查等操作,.默认值是0. check_external_commands=1 #根据自己的情况定这个命令检查时间间隔.默认值是1秒. command_check_interval=10s
2、修改cgi配置文件cgi.cfg.跟修改nagios.cfg一样,只贴出被修改之处: #如有多个用户,中间用逗号隔开 authorized_for_system_information=sery authorized_for_configuration_information=sery authorized_for_system_commands=sery authorized_for_all_services=sery authorized_for_all_hosts=nagiosadmin,sery authorized_for_all_service_commands=sery authorized_for_all_host_commands=sery 在这里指定的用户”sery”可以通过浏览器操纵nagios服务的关闭、重启等各种操作。
3、修改commands.cfg配置文件 这个文件已经包含了发送邮件报警的部分,因此只需要再把短信报警的部分加上就可以了 ###### host-notify-by-sms command definition define command{ command_name host-notify-by-sms command_line /usr/local/bin/sms.pl $CONTACTPAGER$ “$NOTIFICATIONTYPE$ alert – Host $HOSTNAME$ is $HOSTSTATE$” } ###### service-notify-by-sms command definition define command{ command_name service-notify-by-sms command_line /usr/local/bin/sms.pl $CONTACTPAGER$ “$NOTIFICATIONTYPE$: $HOSTALIAS$/$SERVICEDESC$ is $SERVICESTATE$” } 第一个块定义主机报警的内容,即主机发生死机、恢复等情况发送手机短信报警,其接受者和发送内容由”$..$”定义的宏来决定。第二个块定义服务报警内容,即监控的服务或监控的主机资源发生故障时发送手机报警短信。Nagios规定,如果探测到被监控的主机停机或不可达,它就不再探测这个停机主机上的服务。通俗地一点理解:主机都停了,当然服务也跟着停了!另外一个需要注意的地方是命令行(command_line)路径一定要用全路径,这里调用的命令就是我们在全面编写的那个脚本sms.pl。
3、 新增其他配置文件
在主配置文件nagios.cfg中,我们注释了行 cfg_file=/usr/local/nagios/etc/localhost.cfg ,而使用若干单独的配置文件来定义各种对象,这样可以获得维护方便、书写规范等诸多方面的好处。这些单独的配置文件不是自然存在的,我们需要手工创建并添加内容。当然,一开始我们并不是很清楚怎么往这些文件里添加内容,只好回过头去看官方文档,天啦,太分散了,尽然不知道怎么着手了!怎么办?打开文件localhost.cfg-sample,心里基本上就有数了:无非是把这个文件拆分开来,形成多个文件嘛!下面我按新添一个主机进入监控的较优方式添加这些配置文件(当然也可以有其它的顺序,这并不影响监控的效果)。好了,我们先把nagios服务器本身给监控上,这些监控包括:主机存活、web服务监控、磁盘空间监控、负载监控、进程数监控、ip连接数监控。
(1)、定义主机配置文件hosts.cfg define host { host_name nagios-server alias nagios server address 59.26.240.63 contact_groups sagroup check_command check-host-alive max_check_attempts 5 notification_interval 10 notification_period 24×7 notification_options d,u,r } 说明: ● 联系组contact_group没有建立,需在后面的步骤完成。 ● 主机检查命令行一般选择检查主机存活check-host-alive。 ● 最大尝试次数最好不要设置为”1″,一般3-4次比较合理。 ● 通知时间间隔notification_interval 根据自己实际情况设定,它的单位是分钟。 ● 通知选项notification_options 几个值的意思是 d-down,u-unreacheable,r-recovery.
(2)、定义主机组配置文件hostgroups.cfg define hostgroup { hostgroup_name sa-servers alias sa servers members nagios-server } 说明: ● 这个配置文件不是必须的,为了在浏览器里方便归类及察看状态,可以添加这个文件。 ● 主机组的成员必须是在hosts.cfg里已经定义了的,多个主机成员间用逗号分隔。
(3)、定义联系人配置文件contacts.cfg define contact { contact_name sery alias system administrator service_notification_period 24×7 host_notification_period 24×7 service_notification_options w,u,c,r host_notification_options d,u,r service_notification_commands service-notify-by-email,service-notify-by-sms host_notification_commands host-notify-by-email,host-notify-by-sms email sery@163.com pager 13301000018 } 说明: ● 服务通知选项 w-warning,u-unknown,c-critical,r-recovery. ● 主机通知选项 d-down,u-unreacheable,r-recovery。 ● 服务通知命令行及服务通知命令行在配置文件commands.cfg中得到定义,如果有报警发生,则邮件和手机短信一起发送给相关人,即下两行定义的email,pager. ● 收报警信息的邮件和手机,一个人如有2个手机,手机号之间有逗号分隔,邮件也如此。 ● 如果这里定义的用户需要通过浏览器察看他所负责的服务器监控状态的话,还需要 用apache的工具htpasswd增加同名帐号。
(4)、定义联系组配置文件contactgroups.cfg define contactgroup { contactgroup_name sagroup alias system administrator group members sery } 说明: ● 当有多个人行使同样的职责时,定义成组是非常有用的。 ● 多个成员之间用逗号分隔。 ● 成员必须在联系人配置文件(contacts.cfg)已经定义。
(5)、定义服务配置文件 services.cfg define service { host_name nagios-server service_description check-host-alive check_period 24×7 max_check_attempts 4 normal_check_interval 3 retry_check_interval 2 contact_groups sagroup notification_interval 10 notification_period 24×7 notification_options w,u,c,r check_command check-host-alive } define service { host_name nagios-server service_description check_tcp 80 check_period 24×7 max_check_attempts 4 normal_check_interval 3 retry_check_interval 2 contact_groups sagroup notification_interval 10 notification_period 24×7 notification_options w,u,c,r check_command check_tcp!80 } define service{ host_name nagios-server service_description check-disk check_command check_nrpe!check_df max_check_attempts 4 normal_check_interval 3 retry_check_interval 2 check_period 24×7 notification_interval 10 notification_period 24×7 notification_options w,u,c,r contact_groups sagroup } define service{ host_name nagios-server service_description check-load check_command check_nrpe!check_load max_check_attempts 4 normal_check_interval 3 retry_check_interval 2 check_period 24×7 notification_interval 10 notification_period 24×7 notification_options w,u,c,r contact_groups sagroup } define service{ host_name nagios-server service_description total_procs check_command check_nrpe!check_total_procs max_check_attempts 4 normal_check_interval 3 retry_check_interval 2 check_period 24×7 notification_interval 10 notification_period 24×7 notification_options w,u,c,r contact_groups sagroup } 说明: ● 主机名 host_name,必须是主机配置文件hosts.cfg中定义的主机。 ● 检查用的命令 check_command,在命令配置文件中定义或在nrpe配置文件中有定义。 ● 最大重试次数 max_check_attempts 一般设置为3-4次比较好,这样不会因为网络闪断片刻而发生误报。 ● 检查间隔和重试检查间隔的单位是分钟。 ● 通知间隔指探测到故障以后,每隔多少时间发送一次报警信息。 它的单位是分钟。 ● 通知选项跟服务定义配置文件相同。 ● 联系组contact_groups由配置文件contactgroup.cfg定义。 ● 检查主机资源需要安装和配置nrpe,这个过程在后面完成。
#p#
五、部署nrpe
(一)安装nrpe tar zxvf nrpe-2.8.1.tar.gz cd nrpe-2.8.1 ./configure -prefix=/usr/local/nrpe make make install 注:如果在其他被监控机安装nrpe,需要添加系统用户nagios.
(二)复制文件 安装完nrpe后,在安装目录/usr/local/nrpe/libexec只有一个文件check_nrpe,而在nagios插件目录,却缺少这个文件,因此需要把这个文件复制到nagios插件目录;同样,因为nrpe需要调用的诸如check_disk等插件在自己的目录没有,可是这些文件确是nagios插件所存在的,所以也需要从nagios目录复制一份过来。我们把复制过程列举出来: cp /usr/local/nrpe/libexec/check_nrpe /usr/local/nagios/libexec cp /usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_disk /usr/local/nrpe/libexec cp /usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_load /usr/local/nrpe/libexec cp /usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_ping /usr/local/nrpe/libexec cp /usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_procs /usr/local/nrpe/libexec
(三)配置nrpe 安装完nrpe以后,在安装目录并没有可用的配置文件,但我们只需把解压目录的样例文件复制到安装目录,然后修改这个文件. 1、 mkdir /usr/local/nrpe/etc 2、 cp sample-config/nrpe.cfg /usr/local/nrpe/etc 3、 修改配置文件/usr/local/nrpe/etc/nrpe.cfg.该过的地方用粗体显示: pid_file=/var/run/nrpe.pid server_port=5666 #以单独的守护进程运行 server_address=59.26.240.63 nrpe_user=nagios nrpe_group=nagios
allowed_hosts=127.0.0.1,59.26.240.63 dont_blame_nrpe=0
debug=0
command_timeout=60 connection_timeout=300
# The following examples use hardcoded command arguments…
command[check_users]=/usr/local/nrpe/libexec/check_users -w 5 -c 10 command[check_load]=/usr/local/nrpe/libexec/check_load -w 15,10,5 -c 30,25,20 #command[check_hda1]=/usr/local/nrpe/libexec/check_disk -w 20 -c 10 -p /dev/hda1 command[check_df]=/usr/local/nrpe/libexec/check_disk -w 20 -c 10 command[check_zombie_procs]=/usr/local/nrpe/libexec/check_procs -w 5 -c 10 -s Z command[check_total_procs]=/usr/local/nrpe/libexec/check_procs -w 150 -c 200 command[check_ips]=/usr/local/nrpe/libexec/ip_conn.sh 8000 10000
说明: ● allowed_hosts=127.0.0.1,59.26.240.63 必须允许nagios监控服务器可以访问。 ● command[check_df]=/usr/local/nrpe/libexec/check_disk -w 20 -c 10 检查整个服务器的磁盘利用率;如果是freebsd系统,因为其/dev分区为100%,需要排除这个分区,因此其命令行应该为 “command[check_df]=/usr/local/nrpe/libexec/check_disk -x /dev -w 20 -c 10″。 ● command[check_ips]=/usr/local/nrpe/libexec/ip_conn.sh 8000 10000 ip连接数,ip_conn.sh脚本需要自己写,下面给出脚本的内容: #!/bin/sh #if [ $# -ne 2 ] #then # echo “Usage:$0 -w num1 -c num2” #exit 3 #fi
ip_conns=`netstat -an | grep tcp | grep EST | wc -l`
if [ $ip_conns -lt $1 ] then echo “OK -connect counts is $ip_conns” exit 0 fi
if [ $ip_conns -gt $1 -a $ip_conns -lt $2 ] then echo “Warning -connect counts is $ip_conns” exit 1 fi
if [ $ip_conns -gt $2 ] then echo “Critical -connect counts is $ip_conns” exit 2 fi
我在nrpe配置文件nrpe.cfg把脚本所需的两个参数写上了,因此这个脚本就不需判 断两个参数输入值的情况。只要当前ip连接数大于8000,系统就发warning报警,超过10000,则发”critical”报警信息。把这个脚本放在目录/usr/local/nrpe/libexec下,并给于执行权限。
(四)、启动nrpe服务并检验其配置
1、以独立守护进程启动nrpe服务 /usr/local/nrpe/bin/nrpe -c /usr/local/nrpe/etc/nrpe.cfg -d 2、通过察看系统日志,正常启动可以看到如下输出: Mar 2 21:07:18 MONITOR nrpe[23823]: Starting up daemon Mar 2 21:07:18 MONITOR nrpe[23823]: Listening for connections on port 5666 Mar 2 21:07:18 MONITOR nrpe[23823]: Allowing connections from: 127.0.0.1,59.26.240.63 察看端口,也能看见5666端口处于监听状态: [root@MONITOR nrpe]# netstat -an Active Internet connections (servers and established) Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State tcp 0 0 59.26.240.63:5666 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 察看进程: [root@MONITOR nrpe]#ps aux | grep nrpe | grep -v grep nagios 23823 0.0 0.0 4864 924 ? Ss 21:07 0:00 bin/nrpe -c etc/nrpe.cfg -d 3、检查插件功能 (1)检查nrpe服务 [root@MONITOR nrpe]# libexec/check_nrpe -H 59.26.240.63 NRPE v2.8.1 (2)通过nrpe检查主机资源 [root@MONITOR nrpe]# libexec/check_nrpe -H 59.26.240.63 -c check_df DISK OK – free space: / 8241 MB (77% inode=98%); /var 5239 MB (95% inode=99%); /usr 11971 MB (86% inode=97%); /dev/shm 1013 MB (100% inode=99%);| /=2417MB;11218;11228;0;11238 /var=273MB;5792;5802;0;5812 /usr=1807MB;14508;14518;0;14528 /dev/shm=0MB;993;1003;0;1013 [root@MONITOR nrpe]#libexec/check_nrpe -H 59.26.240.63 -c check_ips OK -connect counts is 13956
#p#
六、启动nagios:验证nagios工作状态
1、检查配置: nagios的验证非常准确,凡是不能正确启动nagios,皆可以从错误输出找到答案. /usr/local/nagios/bin/nagios -v /usr/local/nagios/etc/nagios.cfg Reading configuration data…
Running pre-flight check on configuration data… …………… Total Warnings: 0 Total Errors: 0
Things look okay – No serious problems were detected during the pre-flight check 2、启动nagios /usr/local/nagios/bin/nagios -d /usr/local/nagios/etc/nagios.cfg 3、检验监控效果。现在我们监控了本机的web服务,但由于apache服务还没有被启动起来,所以等待片刻后,正常情况下会收到邮件和手机短信报警信息;等后面我们把apache服务起来后,应该能够收到服务已经恢复的报警短信和邮件。
4、创建web验证用户。我们根据前面apache配置文件的验证方法来创建用户: /usr/local/apache/bin/htpasswd -c /usr/local/nagios/etc/htpasswd sery 5、启动apache服务,然后在别的机器的浏览器地址栏输入 http://59.26.240.63/nagios ,再输入第”4″产生的用户名及设定的密码,即可通过web方式察看监控系统当前的状态(浏览器自动刷新屏幕),如下图所示:
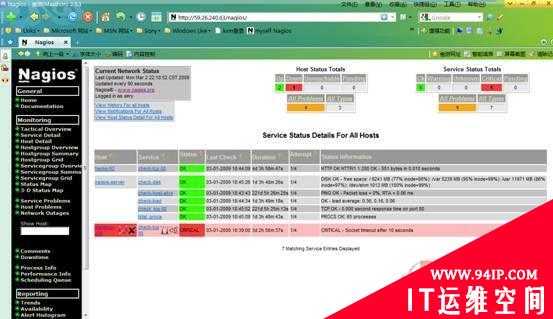
转载请注明:IT运维空间 » 运维技术 » 运维监控Nagios连载3:部署、配置Nagios服务

![[Oracle]复习笔记-SQL部分内容](/zb_users/upload/2023/02/25/20230213095820-63ea09bc55070.jpg)















发表评论