
本文使用的Filebeat是7.7.0的版本,文章将从如下几个方面说明:
Filebeat是什么,可以用来干嘛
Filebeat的原理是怎样的,怎么构成的
Filebeat应该怎么玩
Filebeat是什么
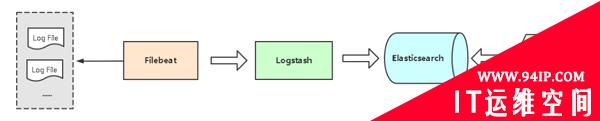
Filebeat和Beats的关系
首先Filebeat是Beats中的一员。
Beats在是一个轻量级日志采集器,其实Beats家族有6个成员,早期的ELK架构中使用Logstash收集、解析日志,但是Logstash对内存、CPU、io等资源消耗比较高。相比Logstash,Beats所占系统的CPU和内存几乎可以忽略不计。
目前Beats包含六种工具:
- Packetbeat:网络数据(收集网络流量数据)
- Metricbeat:指标(收集系统、进程和文件系统级别的CPU和内存使用情况等数据)
- Filebeat:日志文件(收集文件数据)
- Winlogbeat:Windows事件日志(收集Windows事件日志数据)
- Auditbeat:审计数据(收集审计日志)
- Heartbeat:运行时间监控(收集系统运行时的数据)
Filebeat是什么
Filebeat是用于转发和集中日志数据的轻量级传送工具。Filebeat监视您指定的日志文件或位置,收集日志事件,并将它们转发到Elasticsearch或 Logstash进行索引。
Filebeat的工作方式如下:启动Filebeat时,它将启动一个或多个输入,这些输入将在为日志数据指定的位置中查找。对于Filebeat所找到的每个日志,Filebeat都会启动收集器。每个收集器都读取单个日志以获取新内容,并将新日志数据发送到libbeat,libbeat将聚集事件,并将聚集的数据发送到为Filebeat配置的输出。
工作的流程图如下:
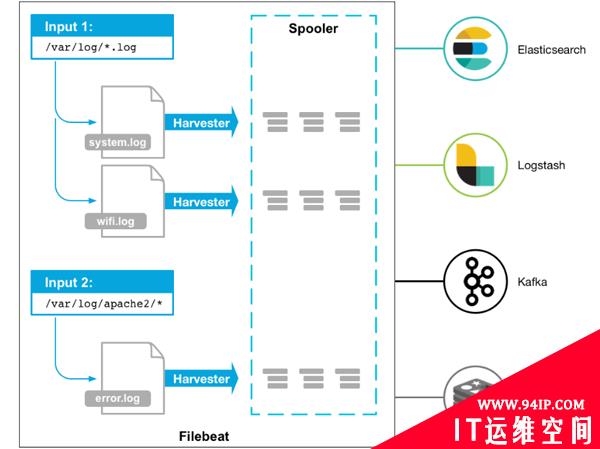
Filebeat和Logstash的关系
因为Logstash是JVM跑的,资源消耗比较大,所以后来作者又用Golang写了一个功能较少但是资源消耗也小的轻量级的logstash-forwarder。不过作者只是一个人,加入http://elastic.co公司以后,因为ES公司本身还收购了另一个开源项目Packetbeat,而这个项目专门就是用Golang的,有整个团队,所以ES公司干脆把logstash-forwarder的开发工作也合并到同一个Golang团队来搞,于是新的项目就叫Filebeat了。
Filebeat原理是什么
Filebeat的构成
Filebeat结构:由两个组件构成,分别是inputs(输入)和harvesters(收集器),这些组件一起工作来跟踪文件并将事件数据发送到您指定的输出,harvester负责读取单个文件的内容。harvester逐行读取每个文件,并将内容发送到输出。为每个文件启动一个harvester。harvester负责打开和关闭文件,这意味着文件描述符在harvester运行时保持打开状态。如果在收集文件时删除或重命名文件,Filebeat将继续读取该文件。这样做的副作用是,磁盘上的空间一直保留到harvester关闭。默认情况下,Filebeat保持文件打开,直到达到close_inactive。
关闭harvester可以会产生的结果:
- 文件处理程序关闭,如果harvester仍在读取文件时被删除,则释放底层资源。
- 只有在scan_frequency结束之后,才会再次启动文件的收集。
- 如果该文件在harvester关闭时被移动或删除,该文件的收集将不会继续。
一个input负责管理harvesters和寻找所有来源读取。如果input类型是log,则input将查找驱动器上与定义的路径匹配的所有文件,并为每个文件启动一个harvester。每个input在它自己的Go进程中运行,Filebeat当前支持多种输入类型。每个输入类型可以定义多次。日志输入检查每个文件,以查看是否需要启动harvester、是否已经在运行harvester或是否可以忽略该文件。
Filebeat如何保存文件的状态
Filebeat保留每个文件的状态,并经常将状态刷新到磁盘中的注册表文件中。该状态用于记住harvester读取的最后一个偏移量,并确保发送所有日志行。如果无法访问输出(如Elasticsearch或Logstash),Filebeat将跟踪最后发送的行,并在输出再次可用时继续读取文件。当Filebeat运行时,每个输入的状态信息也保存在内存中。当Filebeat重新启动时,来自注册表文件的数据用于重建状态,Filebeat在最后一个已知位置继续每个harvester。对于每个输入,Filebeat都会保留它找到的每个文件的状态。由于文件可以重命名或移动,文件名和路径不足以标识文件。对于每个文件,Filebeat存储唯一的标识符,以检测文件是否以前被捕获。
Filebeat何如保证至少一次数据消费
Filebeat保证事件将至少传递到配置的输出一次,并且不会丢失数据。是因为它将每个事件的传递状态存储在注册表文件中。在已定义的输出被阻止且未确认所有事件的情况下,Filebeat将继续尝试发送事件,直到输出确认已接收到事件为止。如果Filebeat在发送事件的过程中关闭,它不会等待输出确认所有事件后再关闭。当Filebeat重新启动时,将再次将Filebeat关闭前未确认的所有事件发送到输出。这样可以确保每个事件至少发送一次,但最终可能会有重复的事件发送到输出。通过设置shutdown_timeout选项,可以将Filebeat配置为在关机前等待特定时间。
Filebeat怎么玩
压缩包方式安装
本文采用压缩包的方式安装,Linux版本,filebeat-7.7.0-linux-x86_64.tar.gz。
curl-L-Ohttps://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/beats/filebeat/filebeat-7.7.0-linux-x86_64.tar.gz tar-xzvffilebeat-7.7.0-linux-x86_64.tar.gz
配置示例文件:filebeat.reference.yml(包含所有未过时的配置项)
配置文件:filebeat.yml
基本命令
详情见官网:https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/beats/filebeat/current/command-line-options.html
export#导出 run#执行(默认执行) test#测试配置 keystore#秘钥存储 modules#模块配置管理 setup#设置初始环境
例如:./filebeat test config #用来测试配置文件是否正确
输入输出
支持的输入组件:
Multilinemessages,Azureeventhub,CloudFoundry,Container,Docker,GooglePub/Sub,HTTPJSON,Kafka,Log,MQTT,NetFlow,Office 365 Management Activity API,Redis,s3,Stdin,Syslog,TCP,UDP(最常用的就是Log)
支持的输出组件:
Elasticsearch,Logstash,Kafka,Redis,File,Console,ElasticCloud,Changetheoutputcodec(最常用的就是Elasticsearch,Logstash)
keystore的使用
keystore主要是防止敏感信息被泄露,比如密码等,像ES的密码,这里可以生成一个key为ES_PWD,值为ES的password的一个对应关系,在使用ES的密码的时候就可以使用${ES_PWD}使用。
- 创建一个存储密码的keystore:filebeat keystore create
- 然后往其中添加键值对,例如:filebeatk eystore add ES_PWD
- 使用覆盖原来键的值:filebeat key store add ES_PWD–force
- 删除键值对:filebeat key store remove ES_PWD
- 查看已有的键值对:filebeat key store list
例如:后期就可以通过${ES_PWD}使用其值,例如:
output.elasticsearch.password:"${ES_PWD}"
filebeat.yml配置(Log输入类型为例)
详情见官网:https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/beats/filebeat/current/filebeat-input-log.html
type:log#input类型为log enable:true#表示是该log类型配置生效 paths:#指定要监控的日志,目前按照Go语言的glob函数处理。没有对配置目录做递归处理,比如配置的如果是: -/var/log/*/*.log#则只会去/var/log目录的所有子目录中寻找以".log"结尾的文件,而不会寻找/var/log目录下以".log"结尾的文件。 recursive_glob.enabled:#启用全局递归模式,例如/foo/**包括/foo,/foo/*,/foo/*/* encoding:#指定被监控的文件的编码类型,使用plain和utf-8都是可以处理中文日志的 exclude_lines:['^DBG']#不包含匹配正则的行 include_lines:['^ERR','^WARN']#包含匹配正则的行 harvester_buffer_size:16384#每个harvester在获取文件时使用的缓冲区的字节大小 max_bytes:10485760#单个日志消息可以拥有的最大字节数。max_bytes之后的所有字节都被丢弃而不发送。默认值为10MB(10485760) exclude_files:['\.gz$']#用于匹配希望Filebeat忽略的文件的正则表达式列表 ingore_older:0#默认为0,表示禁用,可以配置2h,2m等,注意ignore_older必须大于close_inactive的值.表示忽略超过设置值未更新的 文件或者文件从来没有被harvester收集 close_*#close_*配置选项用于在特定标准或时间之后关闭harvester。关闭harvester意味着关闭文件处理程序。如果在harvester关闭 后文件被更新,则在scan_frequency过后,文件将被重新拾取。但是,如果在harvester关闭时移动或删除文件,Filebeat将无法再次接收文件 ,并且harvester未读取的任何数据都将丢失。 close_inactive#启动选项时,如果在制定时间没有被读取,将关闭文件句柄 读取的最后一条日志定义为下一次读取的起始点,而不是基于文件的修改时间 如果关闭的文件发生变化,一个新的harverster将在scan_frequency运行后被启动 建议至少设置一个大于读取日志频率的值,配置多个prospector来实现针对不同更新速度的日志文件 使用内部时间戳机制,来反映记录日志的读取,每次读取到最后一行日志时开始倒计时使用2h5m来表示 close_rename#当选项启动,如果文件被重命名和移动,filebeat关闭文件的处理读取 close_removed#当选项启动,文件被删除时,filebeat关闭文件的处理读取这个选项启动后,必须启动clean_removed close_eof#适合只写一次日志的文件,然后filebeat关闭文件的处理读取 close_timeout#当选项启动时,filebeat会给每个harvester设置预定义时间,不管这个文件是否被读取,达到设定时间后,将被关闭 close_timeout不能等于ignore_older,会导致文件更新时,不会被读取如果output一直没有输出日志事件,这个timeout是不会被启动的, 至少要要有一个事件发送,然后haverter将被关闭 设置0表示不启动 clean_inactived#从注册表文件中删除先前收获的文件的状态 设置必须大于ignore_older+scan_frequency,以确保在文件仍在收集时没有删除任何状态 配置选项有助于减小注册表文件的大小,特别是如果每天都生成大量的新文件 此配置选项也可用于防止在Linux上重用inode的Filebeat问题 clean_removed#启动选项后,如果文件在磁盘上找不到,将从注册表中清除filebeat 如果关闭closeremoved必须关闭cleanremoved scan_frequency#prospector检查指定用于收获的路径中的新文件的频率,默认10s tail_files:#如果设置为true,Filebeat从文件尾开始监控文件新增内容,把新增的每一行文件作为一个事件依次发送, 而不是从文件开始处重新发送所有内容。 symlinks:#符号链接选项允许Filebeat除常规文件外,可以收集符号链接。收集符号链接时,即使报告了符号链接的路径, Filebeat也会打开并读取原始文件。 backoff:#backoff选项指定Filebeat如何积极地抓取新文件进行更新。默认1s,backoff选项定义Filebeat在达到EOF之后 再次检查文件之间等待的时间。 max_backoff:#在达到EOF之后再次检查文件之前Filebeat等待的最长时间 backoff_factor:#指定backoff尝试等待时间几次,默认是2 harvester_limit:#harvester_limit选项限制一个prospector并行启动的harvester数量,直接影响文件打开数 tags#列表中添加标签,用过过滤,例如:tags:["json"] fields#可选字段,选择额外的字段进行输出可以是标量值,元组,字典等嵌套类型 默认在sub-dictionary位置 filebeat.inputs: fields: app_id:query_engine_12 fields_under_root#如果值为ture,那么fields存储在输出文档的顶级位置 multiline.pattern#必须匹配的regexp模式 multiline.negate#定义上面的模式匹配条件的动作是否定的,默认是false 假如模式匹配条件'^b',默认是false模式,表示讲按照模式匹配进行匹配将不是以b开头的日志行进行合并 如果是true,表示将不以b开头的日志行进行合并 multiline.match#指定Filebeat如何将匹配行组合成事件,在之前或者之后,取决于上面所指定的negate multiline.max_lines#可以组合成一个事件的最大行数,超过将丢弃,默认500 multiline.timeout#定义超时时间,如果开始一个新的事件在超时时间内没有发现匹配,也将发送日志,默认是5s max_procs#设置可以同时执行的最大CPU数。默认值为系统中可用的逻辑CPU的数量。 name#为该filebeat指定名字,默认为主机的hostname
实例一:Logstash作为输出
filebeat.yml配置:
#===========================Filebeatinputs============================= filebeat.inputs: #Each-isaninput.Mostoptionscanbesetattheinputlevel,so #youcanusedifferentinputsforvariousconfigurations. #Belowaretheinputspecificconfigurations. -type:log #Changetotruetoenablethisinputconfiguration. enabled:true #Pathsthatshouldbecrawledandfetched.Globbasedpaths. paths:#配置多个日志路径 -/var/logs/es_aaa_index_search_slowlog.log -/var/logs/es_bbb_index_search_slowlog.log -/var/logs/es_ccc_index_search_slowlog.log -/var/logs/es_ddd_index_search_slowlog.log #-c:\programdata\elasticsearch\logs\* #Excludelines.Alistofregularexpressionstomatch.Itdropsthelinesthatare #matchinganyregularexpressionfromthelist. #exclude_lines:['^DBG'] #Includelines.Alistofregularexpressionstomatch.Itexportsthelinesthatare #matchinganyregularexpressionfromthelist. #include_lines:['^ERR','^WARN'] #Excludefiles.Alistofregularexpressionstomatch.Filebeatdropsthefilesthat #arematchinganyregularexpressionfromthelist.Bydefault,nofilesaredropped. #exclude_files:['.gz$'] #Optionaladditionalfields.Thesefieldscanbefreelypicked #toaddadditionalinformationtothecrawledlogfilesforfiltering #fields: #level:debug #review:1 ###Multilineoptions #Multilinecanbeusedforlogmessagesspanningmultiplelines.Thisiscommon #forJavaStackTracesorC-LineContinuation #TheregexpPatternthathastobematched.Theexamplepatternmatchesalllinesstartingwith[ #multiline.pattern:^\[ #Definesifthepatternsetunderpatternshouldbenegatedornot.Defaultisfalse. #multiline.negate:false #Matchcanbesetto"after"or"before".Itisusedtodefineiflinesshouldbeappendtoapattern #thatwas(not)matchedbeforeorafteroraslongasapatternisnotmatchedbasedonnegate. #Note:AfteristheequivalenttopreviousandbeforeistheequivalenttotonextinLogstash #multiline.match:after #================================Outputs===================================== #-----------------------------Logstashoutput-------------------------------- output.logstash: #TheLogstashhosts#配多个logstash使用负载均衡机制 hosts:["192.168.110.130:5044","192.168.110.131:5044","192.168.110.132:5044","192.168.110.133:5044"] loadbalance:true#使用了负载均衡 #OptionalSSL.Bydefaultisoff. #ListofrootcertificatesforHTTPSserververifications #ssl.certificate_authorities:["/etc/pki/root/ca.pem"] #CertificateforSSLclientauthentication #ssl.certificate:"/etc/pki/client/cert.pem" #ClientCertificateKey #ssl.key:"/etc/pki/client/cert.key"
./filebeat -e #启动filebeat
Logstash的配置:
input{
beats{
port=>5044
}
}
output{
elasticsearch{
hosts=>["http://192.168.110.130:9200"]#这里可以配置多个
index=>"query-%{yyyyMMdd}"
}
}
实例二:Elasticsearch作为输出
filebeat.yml的配置:
######################FilebeatConfigurationExample#########################
#Thisfileisanexampleconfigurationfilehighlightingonlythemostcommon
#options.Thefilebeat.reference.ymlfilefromthesamedirectorycontainsallthe
#supportedoptionswithmorecomments.Youcanuseitasareference.
#
#Youcanfindthefullconfigurationreferencehere:
#https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/beats/filebeat/index.html
#Formoreavailablemodulesandoptions,pleaseseethefilebeat.reference.ymlsample
#configurationfile.
#===========================Filebeatinputs=============================
filebeat.inputs:
#Each-isaninput.Mostoptionscanbesetattheinputlevel,so
#youcanusedifferentinputsforvariousconfigurations.
#Belowaretheinputspecificconfigurations.
-type:log
#Changetotruetoenablethisinputconfiguration.
enabled:true
#Pathsthatshouldbecrawledandfetched.Globbasedpaths.
paths:
-/var/logs/es_aaa_index_search_slowlog.log
-/var/logs/es_bbb_index_search_slowlog.log
-/var/logs/es_ccc_index_search_slowlog.log
-/var/logs/es_dddd_index_search_slowlog.log
#-c:\programdata\elasticsearch\logs\*
#Excludelines.Alistofregularexpressionstomatch.Itdropsthelinesthatare
#matchinganyregularexpressionfromthelist.
#exclude_lines:['^DBG']
#Includelines.Alistofregularexpressionstomatch.Itexportsthelinesthatare
#matchinganyregularexpressionfromthelist.
#include_lines:['^ERR','^WARN']
#Excludefiles.Alistofregularexpressionstomatch.Filebeatdropsthefilesthat
#arematchinganyregularexpressionfromthelist.Bydefault,nofilesaredropped.
#exclude_files:['.gz$']
#Optionaladditionalfields.Thesefieldscanbefreelypicked
#toaddadditionalinformationtothecrawledlogfilesforfiltering
#fields:
#level:debug
#review:1
###Multilineoptions
#Multilinecanbeusedforlogmessagesspanningmultiplelines.Thisiscommon
#forJavaStackTracesorC-LineContinuation
#TheregexpPatternthathastobematched.Theexamplepatternmatchesalllinesstartingwith[
#multiline.pattern:^\[
#Definesifthepatternsetunderpatternshouldbenegatedornot.Defaultisfalse.
#multiline.negate:false
#Matchcanbesetto"after"or"before".Itisusedtodefineiflinesshouldbeappendtoapattern
#thatwas(not)matchedbeforeorafteroraslongasapatternisnotmatchedbasedonnegate.
#Note:AfteristheequivalenttopreviousandbeforeistheequivalenttotonextinLogstash
#multiline.match:after
#=============================Filebeatmodules===============================
filebeat.config.modules:
#Globpatternforconfigurationloading
path:${path.config}/modules.d/*.yml
#Settotruetoenableconfigreloading
reload.enabled:false
#Periodonwhichfilesunderpathshouldbecheckedforchanges
#reload.period:10s
#====================Elasticsearchtemplatesetting==========================
#================================General=====================================
#Thenameoftheshipperthatpublishesthenetworkdata.Itcanbeusedtogroup
#allthetransactionssentbyasingleshipperinthewebinterface.
name:filebeat222
#Thetagsoftheshipperareincludedintheirownfieldwitheach
#transactionpublished.
#tags:["service-X","web-tier"]
#Optionalfieldsthatyoucanspecifytoaddadditionalinformationtothe
#output.
#fields:
#env:staging
#cloud.auth:
#================================Outputs=====================================
#--------------------------Elasticsearchoutput------------------------------
output.elasticsearch:
#Arrayofhoststoconnectto.
hosts:["192.168.110.130:9200","92.168.110.131:9200"]
#Protocol-either`http`(default)or`https`.
#protocol:"https"
#Authenticationcredentials-eitherAPIkeyorusername/password.
#api_key:"id:api_key"
username:"elastic"
password:"${ES_PWD}"#通过keystore设置密码
./filebeat -e #启动Filebeat
查看Elasticsearch集群,有一个默认的索引名字filebeat-%{[beat.version]}-%{+yyyy.MM.dd}
Filebeat模块
官网:https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/beats/filebeat/current/filebeat-modules.html
这里我使用Elasticsearch模式来解析ES的慢日志查询,操作步骤如下,其他的模块操作也一样:
前提:安装好Elasticsearch和Kibana两个软件,然后使用Filebeat。
具体的操作官网有:https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/beats/filebeat/current/filebeat-modules-quickstart.html
第一步,配置filebeat.yml文件:
#==============================Kibana=====================================
#StartingwithBeatsversion6.0.0,thedashboardsareloadedviatheKibanaAPI.
#ThisrequiresaKibanaendpointconfiguration.
setup.kibana:
#KibanaHost
#Schemeandportcanbeleftoutandwillbesettothedefault(httpand5601)
#Incaseyouspecifyandadditionalpath,theschemeisrequired:http://localhost:5601/path
#IPv6addressesshouldalwaysbedefinedas:https://[2001:db8::1]:5601
host:"192.168.110.130:5601"#指定kibana
username:"elastic"#用户
password:"${ES_PWD}"#密码,这里使用了keystore,防止明文密码
#KibanaSpaceID
#IDoftheKibanaSpaceintowhichthedashboardsshouldbeloaded.Bydefault,
#theDefaultSpacewillbeused.
#space.id:
#================================Outputs=====================================
#Configurewhatoutputtousewhensendingthedatacollectedbythebeat.
#--------------------------Elasticsearchoutput------------------------------
output.elasticsearch:
#Arrayofhoststoconnectto.
hosts:["192.168.110.130:9200","192.168.110.131:9200"]
#Protocol-either`http`(default)or`https`.
#protocol:"https"
#Authenticationcredentials-eitherAPIkeyorusername/password.
#api_key:"id:api_key"
username:"elastic"#es的用户
password:"${ES_PWD}"#es的密码
#这里不能指定index,因为我没有配置模板,会自动生成一个名为filebeat-%{[beat.version]}-%{+yyyy.MM.dd}的索引
第二步,配置Elasticsearch的慢日志路径:
cdfilebeat-7.7.0-linux-x86_64/modules.d
vim elasticsearch.yml:

第三步,生效ES模块:
./filebeatmoduleselasticsearch
查看生效的模块:
./filebeatmoduleslist
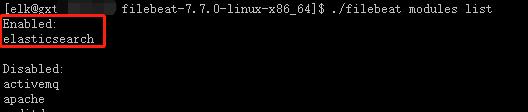
第四步,初始化环境:
./filebeatsetup-e
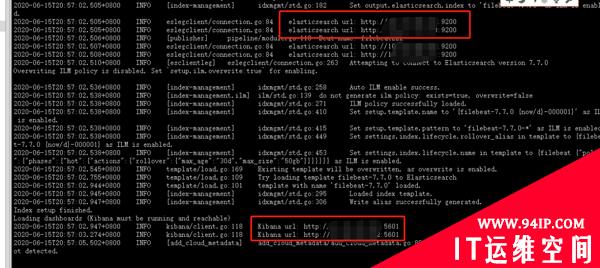
第五步,启动Filebeat:
./filebeat-e
查看Elasticsearch集群,如下图所示,把慢日志查询的日志都自动解析出来了:

到这里,Elasticsearch这个module就实验成功了。
转载请注明:IT运维空间 » 运维技术 » 一篇文章教你搞懂日志采集利器Filebeat

![[Oracle]复习笔记-SQL部分内容](/zb_users/upload/2023/02/25/20230213095820-63ea09bc55070.jpg)





![[ORACLE]查看SQL绑定变量具体值 查看SQL绑定变量值](https://94ip.com/zb_users/theme/ydconcise/include/random/5.jpg)





发表评论