
老规矩,先上案例代码,我们按照这个案例一步一步的搞定Mybatis源码。
publicclassMybatisApplication{
publicstaticfinalStringURL="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mblog";
publicstaticfinalStringUSER="root";
publicstaticfinalStringPASSWORD="123456";
publicstaticvoidmain(String[]args){
Stringresource="mybatis-config.xml";
InputStreaminputStream=null;
SqlSessionsqlSession=null;
try{
inputStream=Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactorysqlSessionFactory=newSqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
sqlSession=sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
UserMapperuserMapper=sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
System.out.println(userMapper.selectById(1));
}catch(Exceptione){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
try{
inputStream.close();
}catch(IOExceptione){
e.printStackTrace();
}
sqlSession.close();
}
}
由于很多小伙伴在催,说Mybatis源码系列好像何时才有下文了,为此老田熬夜写了这篇。
继续开撸~~
SqlSessionsqlSession=sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
前面那篇文章已经分析了,这里的sqlSessionFactory其实就是DefaultSqlSessionFactory。
所以这里,我们就从DefaultSqlSessionFactory里的openSession方法开始。
publicclassDefaultSqlSessionFactoryimplementsSqlSessionFactory{
privatefinalConfigurationconfiguration;
publicDefaultSqlSessionFactory(Configurationconfiguration){
this.configuration=configuration;
}
//创建session,这个方法直接调用本类中的另外一个方法
@Override
publicSqlSessionopenSession(){
returnopenSessionFromDataSource(configuration.getDefaultExecutorType(),null,false);
}
//其实是调用这个方法
privateSqlSessionopenSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorTypeexecType,TransactionIsolationLevellevel,booleanautoCommit){
Transactiontx=null;
try{
//对应xml标签<environments>,这个在配置文件解析的时候就已经存放到configuration中了。
finalEnvironmentenvironment=configuration.getEnvironment();
finalTransactionFactorytransactionFactory=getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);
tx=transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(),level,autoCommit);
//创建一个executor来执行SQL
finalExecutorexecutor=configuration.newExecutor(tx,execType);
//这里也说明了,为什么我们代码里的SqlSession是DefaultSqlSession
returnnewDefaultSqlSession(configuration,executor,autoCommit);
}catch(Exceptione){
closeTransaction(tx);//mayhavefetchedaconnectionsoletscallclose()
throwExceptionFactory.wrapException("Erroropeningsession.Cause:"+e,e);
}finally{
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
privateTransactionFactorygetTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(Environmentenvironment){
if(environment==null||environment.getTransactionFactory()==null){
returnnewManagedTransactionFactory();
}
returnenvironment.getTransactionFactory();
}
这个方法中的主要内容有:
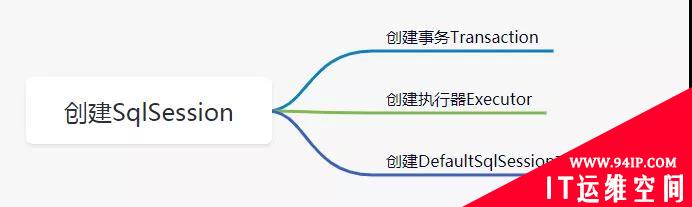
下面我们就来逐个攻破。
创建事务Transaction
事务工厂类型可以配置为JDBC类型或者MANAGED类型。
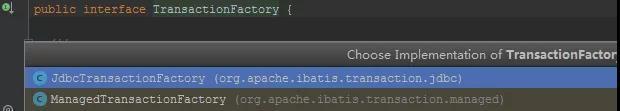
JdbcTransactionFactory生产JdbcTransaction。
ManagedTransactionFactory生产ManagedTransaction。
如果配置的JDBC,则会使用Connection对象的commit()、rollback()、close()方法来管理事务。
如果我们配置的是MANAGED,会把事务交给容器来管理,比如JBOSS,Weblogic。因为我们是本地跑的程序,如果配置成MANAGED就会不有任何事务。
但是,如果我们项目中是Spring集成Mybatis,则没有必要配置事务,因为我们会直接在applicationContext.xml里配置数据源和事务管理器,从而覆盖Mybatis的配置。
创建执行器Executor
调用configuration的newExecutor方法创建Executor。
finalExecutorexecutor=configuration.newExecutor(tx,execType);
//Configuration中
publicExecutornewExecutor(Transactiontransaction,ExecutorTypeexecutorType){
executorType=executorType==null?defaultExecutorType:executorType;
executorType=executorType==null?ExecutorType.SIMPLE:executorType;
Executorexecutor;
//第一步
if(ExecutorType.BATCH==executorType){
executor=newBatchExecutor(this,transaction);
}elseif(ExecutorType.REUSE==executorType){
executor=newReuseExecutor(this,transaction);
}else{
executor=newSimpleExecutor(this,transaction);
}
//第二步
if(cacheEnabled){
executor=newCachingExecutor(executor);
}
//第三步
executor=(Executor)interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);
returnexecutor;
}
此方法分三个步骤。
第一步:创建执行器
Executor的基本类型有三种:
publicenumExecutorType{
SIMPLE,REUSE,BATCH
}
SIMPLE为默认类型。
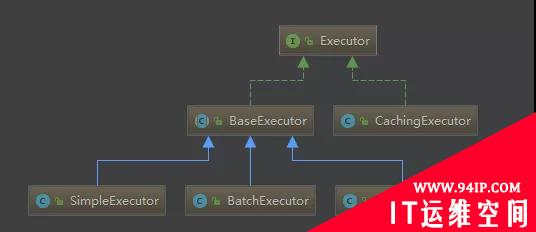
为什么要让抽象类BaseExecutor实现Executor接口,然后让具体实现类继承抽象类呢?
这就是模板方法模式的实现。
模板方法模式就是定义一个算法骨架,并允许子类为一个或者多个步骤提供实现。模板方法是得子类可以再不改变算法结构的情况下,重新定义算法的某些步骤。
抽象方法是在子类汇总实现的,每种执行器自己实现自己的逻辑,BaseExecutor最终会调用到具体的子类中。
抽象方法
protectedabstractintdoUpdate(MappedStatementms,Objectparameter)throwsSQLException; protectedabstractList<BatchResult>doFlushStatements(booleanisRollback)throwsSQLException; protectedabstract<E>List<E>doQuery(MappedStatementms,Objectparameter,RowBoundsrowBounds,ResultHandlerresultHandler,BoundSqlboundSql)throwsSQLException; protectedabstract<E>Cursor<E>doQueryCursor(MappedStatementms,Objectparameter,RowBoundsrowBounds,BoundSqlboundSql)throwsSQLException;
第二步:缓存装饰
在上面代码中的第二步
if(cacheEnabled){
executor=newCachingExecutor(executor);
}
如果cacheEnabled=true,会用装饰器设计模式对Executor进行装饰。
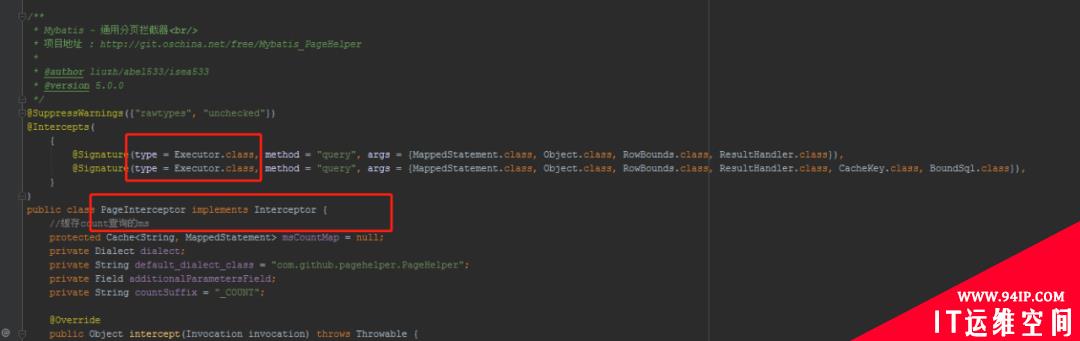
第三步:插件代理缓存装饰完后,就会执行
executor=(Executor)interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);
这里会对Executor植入插件逻辑。
比如:分页插件中就需要把插件植入的Executor
好了,到此,执行器创建的就搞定了。
创建DefaultSqlSession对象
把前面解析配置文件创建的Configuration对象和创建的执行器Executor赋给DefaultSqlSession中的属性。
publicDefaultSqlSession(Configurationconfiguration,Executorexecutor,booleanautoCommit){
this.configuration=configuration;
this.executor=executor;
this.dirty=false;
this.autoCommit=autoCommit;
}
到这里,SqlSession(DefaultSqlSession)对象就创建完毕。
总结
本文我们讲了如何创建SqlSession的几个步骤,最后我们获得一个DefaultSqlSession对象,里面包含了执行器Executor和配置对象Configuration。Executor是SQL的实际执行对象。Configuration里保存着配置文件内容。
本文源码分析的整个流程如下图:
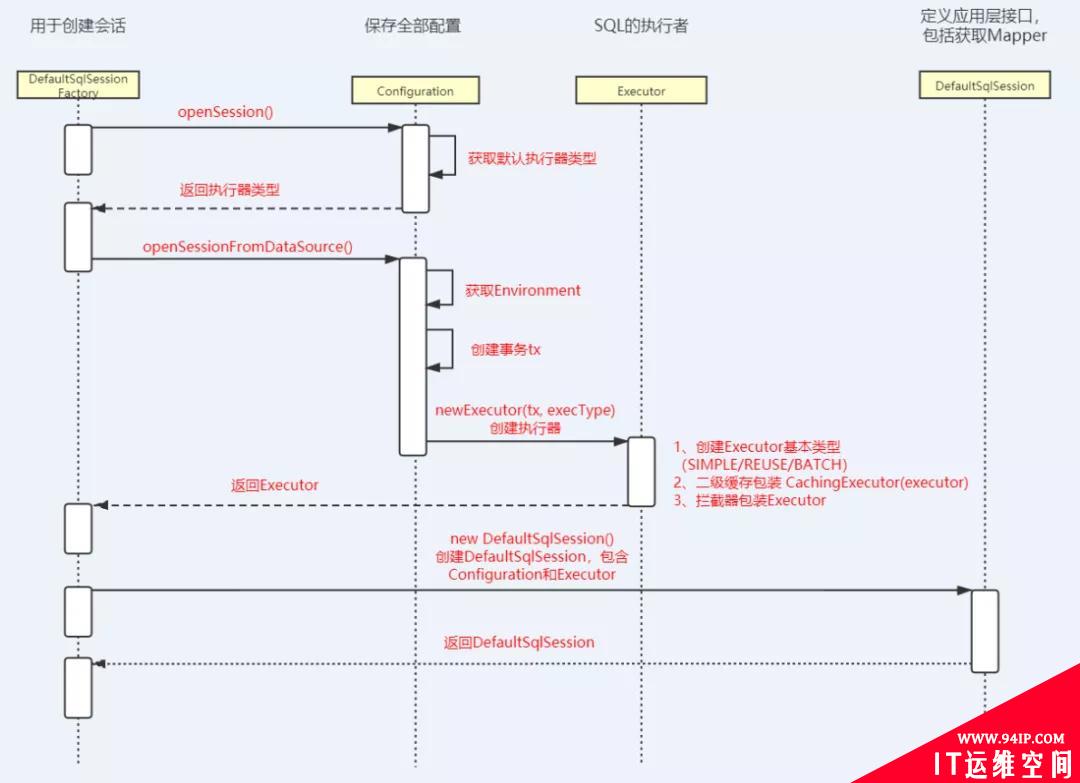
转载请注明:IT运维空间 » 运维技术 » 如何扒开 SqlSession 的外衣

![[Oracle]复习笔记-SQL部分内容](/zb_users/upload/2023/02/25/20230213095820-63ea09bc55070.jpg)














发表评论